Sensational Tips About How To Control Severe Bleeding

With a severe cut or injury, you need to take action to stop the bleeding immediately.
How to control severe bleeding. Instruct the casualty to do this if possible. This can trigger anxiety and fear, but bleeding has a healing purpose. Make sure the scene is safe for you to help the injured person.
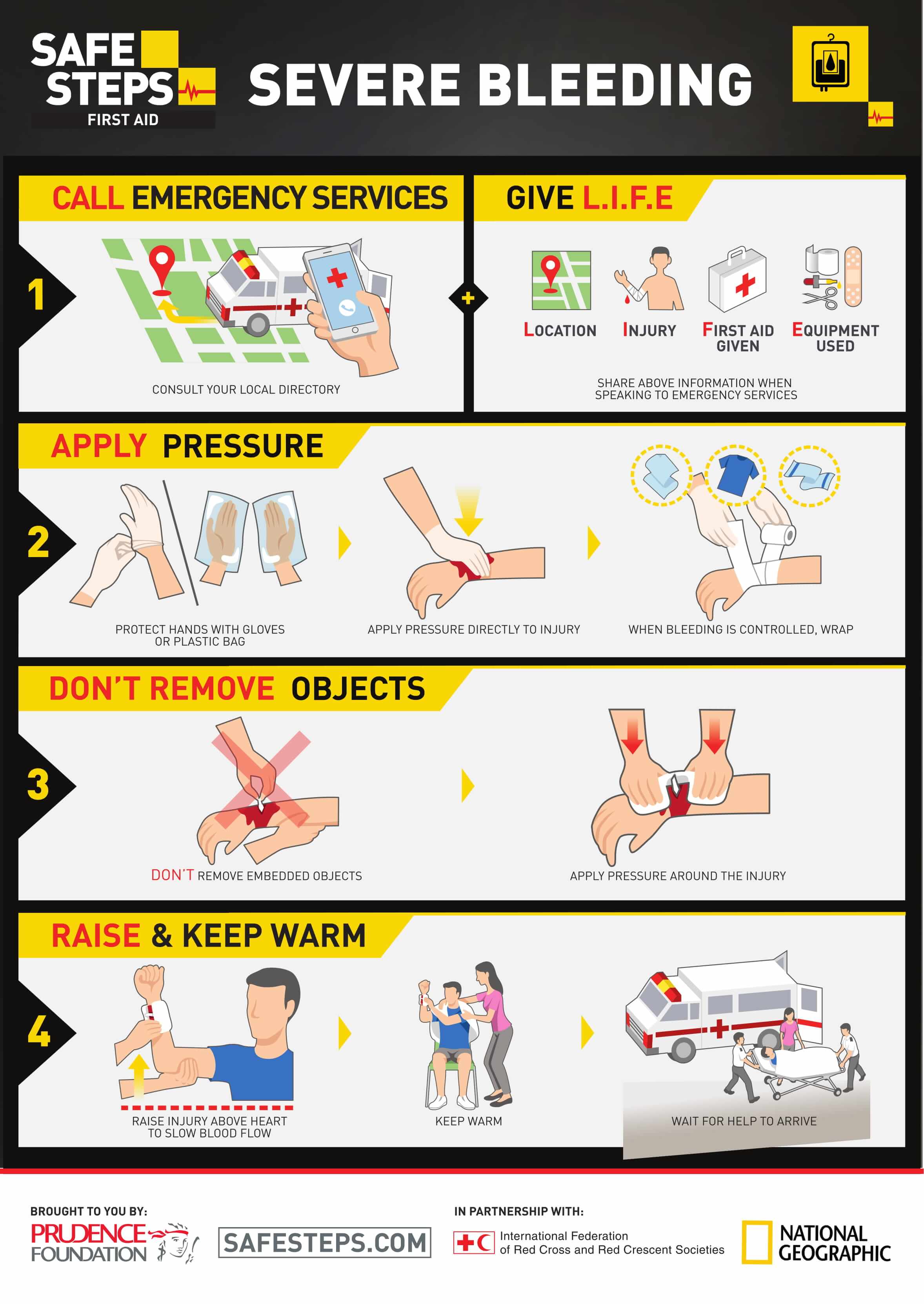
Treatment for severe bleeding. 4 first aid steps everyone should know. If not, have someone else call so you can focus on finding the source of the bleeding.
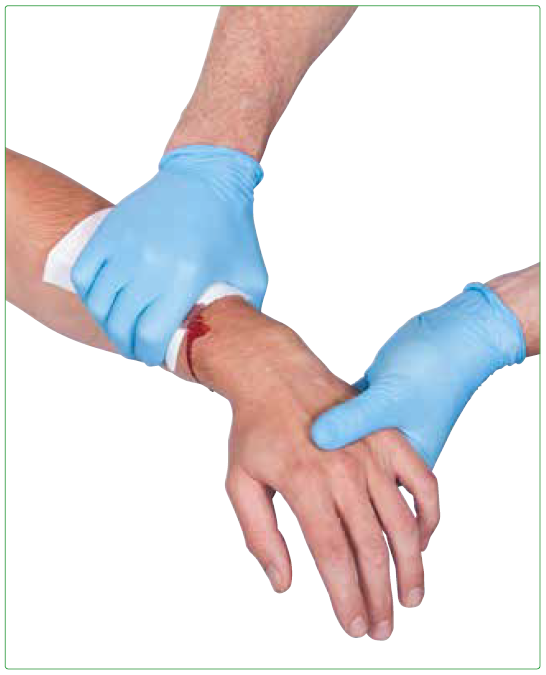
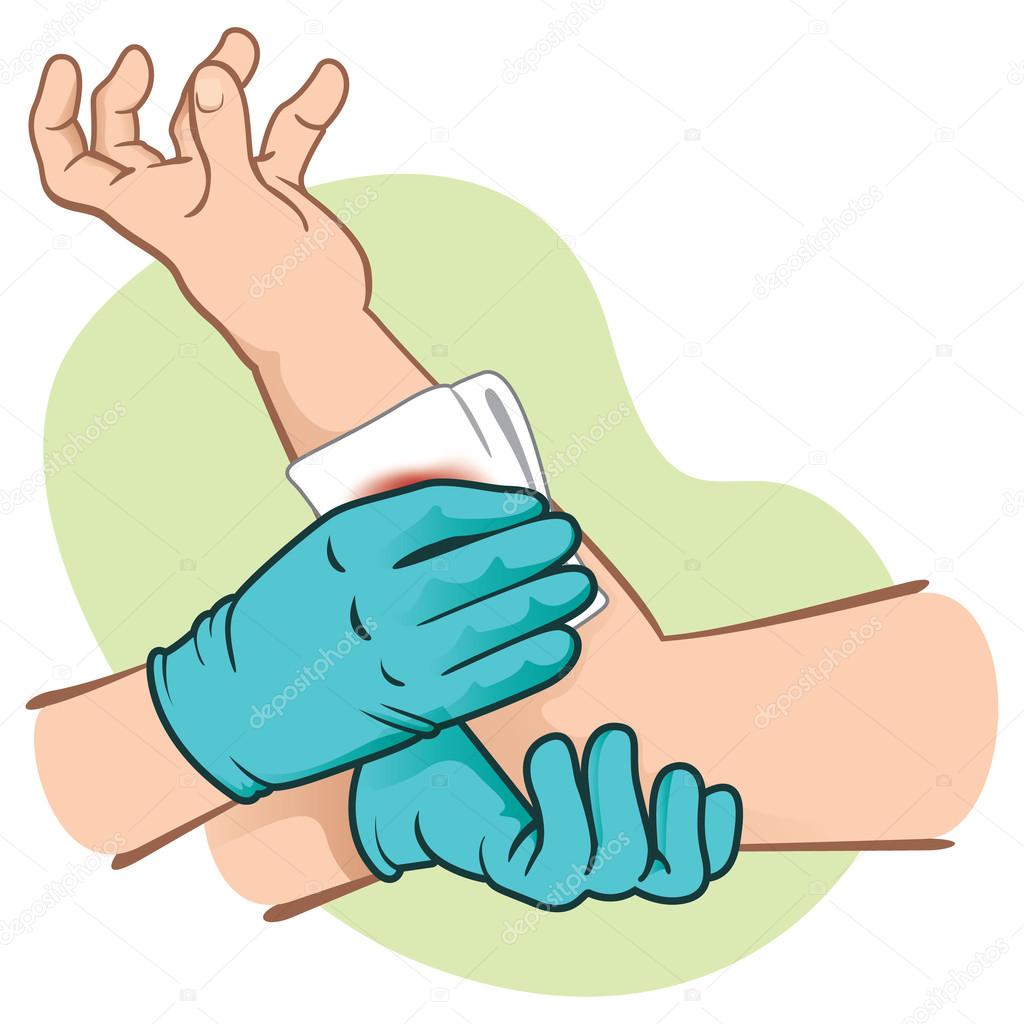
Move the person to safety if you can. The first aid provider should apply direct manual compression rather than applying a pressure dressing to a severe bleed. Squeeze the wound edges together if possible.
Advise the patient that this will cause pain. Do you know what to do? Take a deep breath, you can do this.
Updated on september 18, 2021. Injuries and certain medical conditions can result in bleeding. Stopping the bleed.
Help the patient to lie down. Stop the bleed, a simple course to teach people how to control bleeding during the first moments after a serious injury, is gaining momentum. Call paramedics for help immediately.
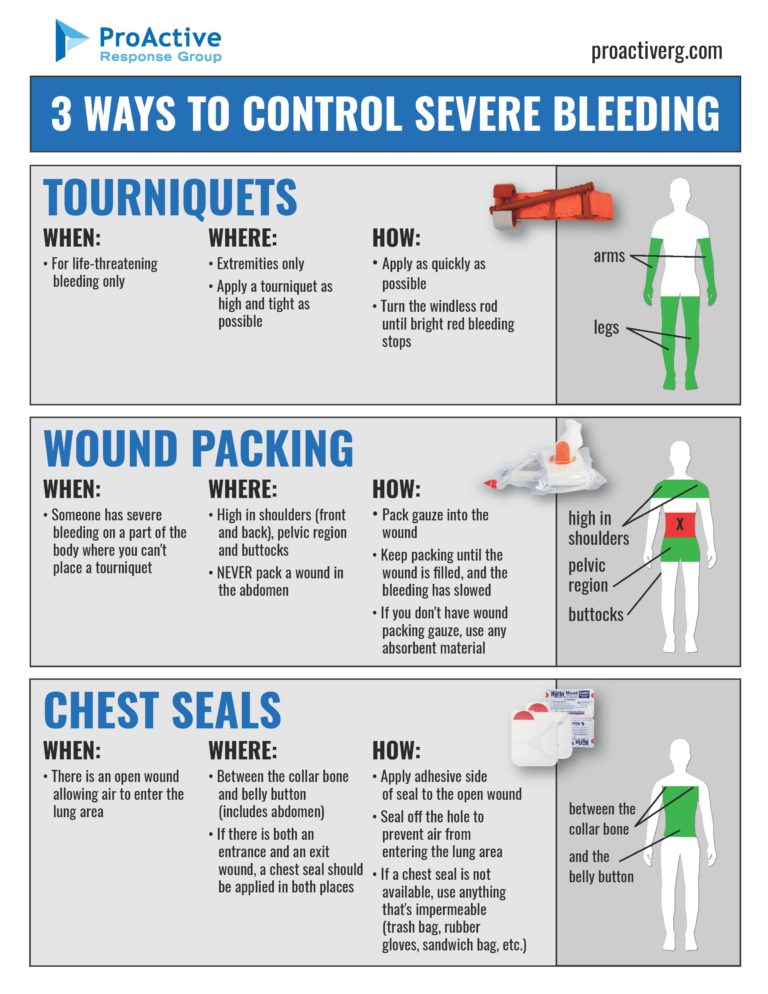
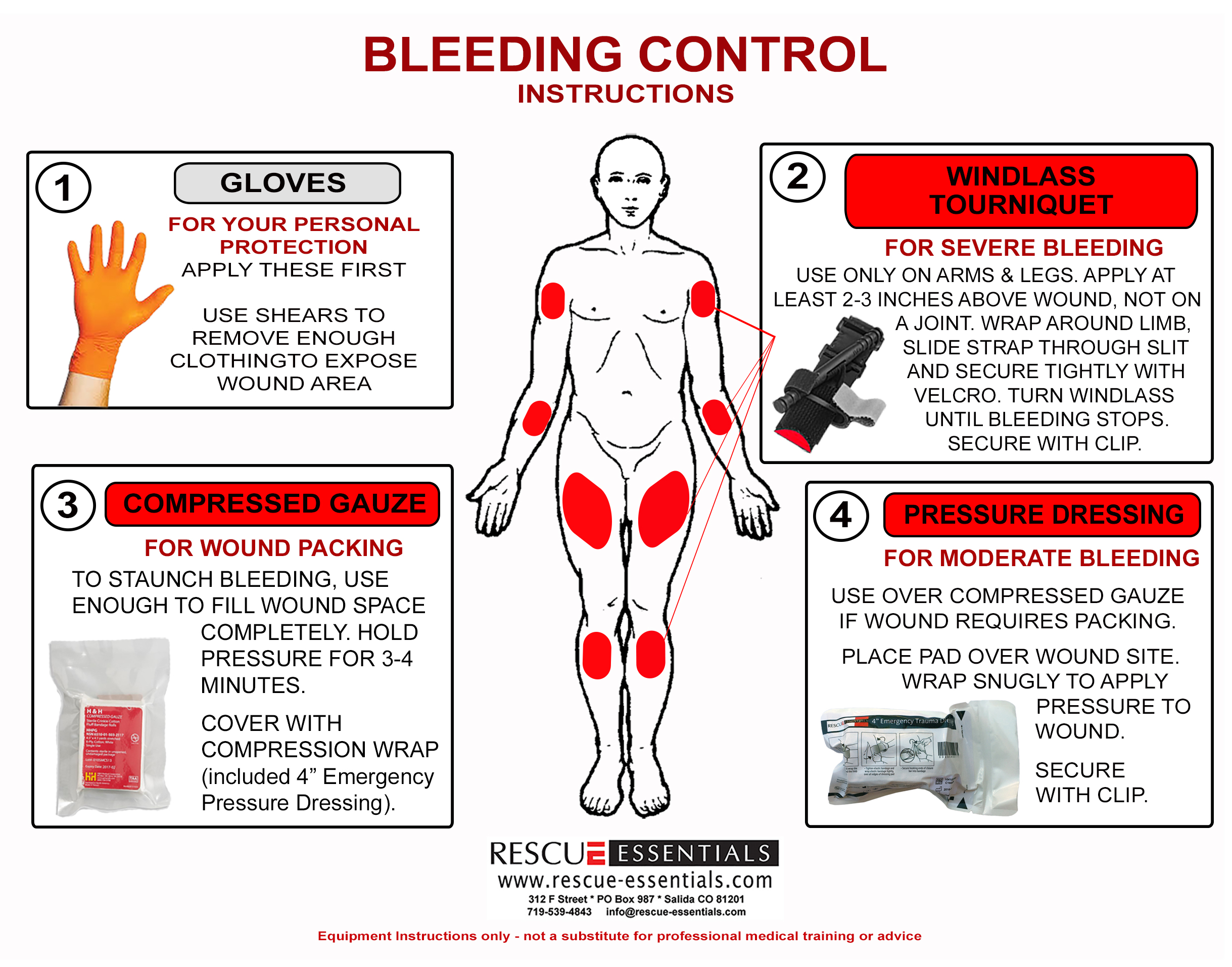
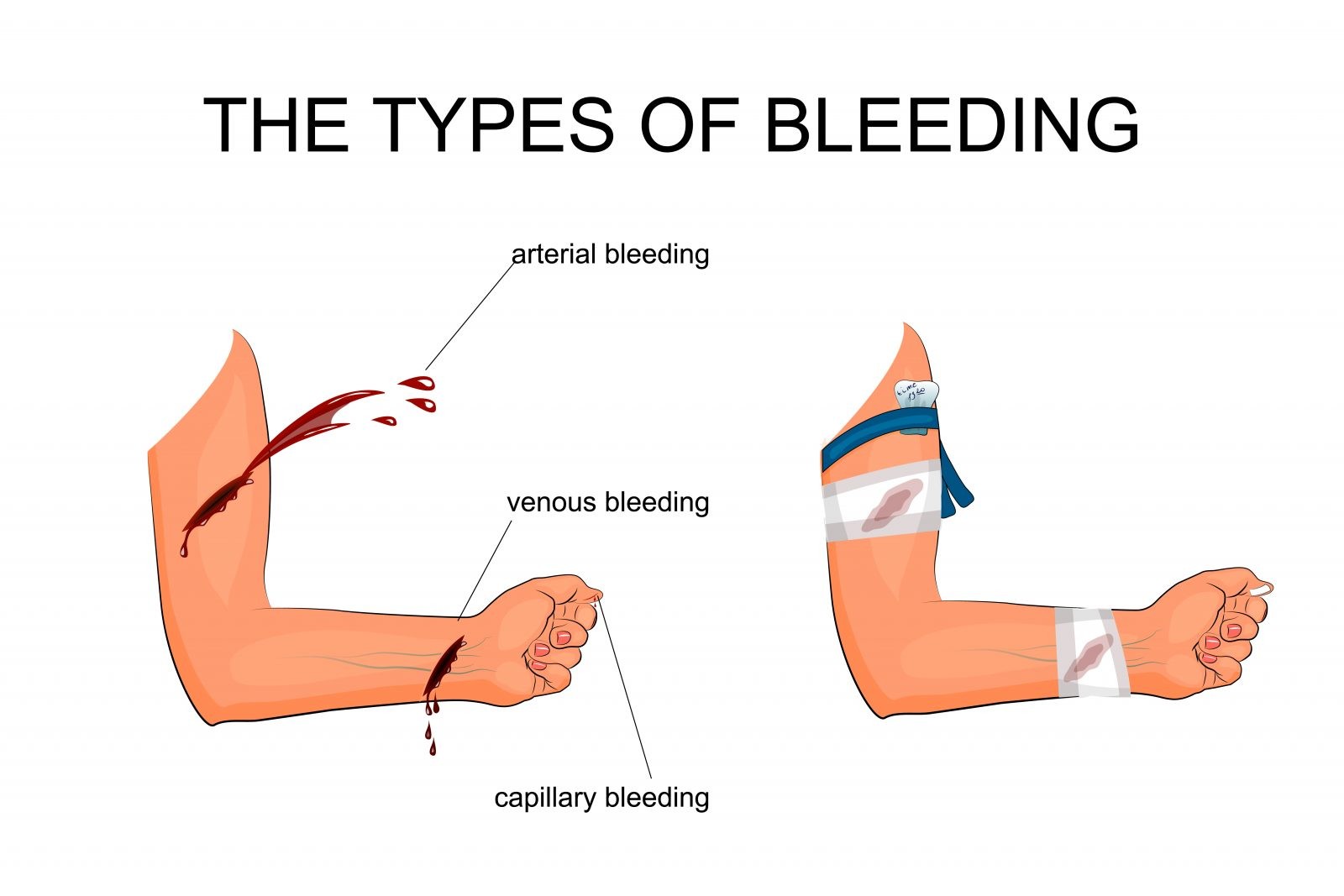
You are acting as a “plug” to stop the blood escaping. The bleeding is not on a limb, remove existing dressings and apply a haemostatic dressing (if available) in or directly over the wound. Bleeding, also called hemorrhage, is the name used to describe blood loss.
If there’s no immediate danger: Once the bleeding stops, tie a cloth, gauze or towel tightly around the wound without cutting off circulation. A medical background isn't necessary to learn the basics of.
Don't move the injured person except if needed to avoid further injury. First aid advice for bleeding wounds including nose bleeds, severe bleeding and shock including what to do and when to get medical assistance. Apply direct pressure over and around the wound using a pad or your hands.
Treatment may involve the following: Knowing how to control bleeding can make the difference between life and death for you or a loved one. In an emergency, your fight or flight response will kick in and hormones like adrenaline will.