Real Info About How To Detect Genetic Disorders

Other laboratory tests that measure the levels of certain substances in blood and urine can also help suggest a diagnosis.
How to detect genetic disorders. Genetic testing is a type of medical test that identifies changes in chromosomes, genes or proteins. How are genetic conditions treated or managed? Overall, only 30% of patients completed genetic testing.
Multiple doctors and multiple examinations could not figure out why lauri sieben had spent much of her life “never. Help you understand whether an inherited health condition may affect you, your child or another family member, and help you decide whether to have children. Traditionally this is done looking at markers in blood or by invasive testing such as.
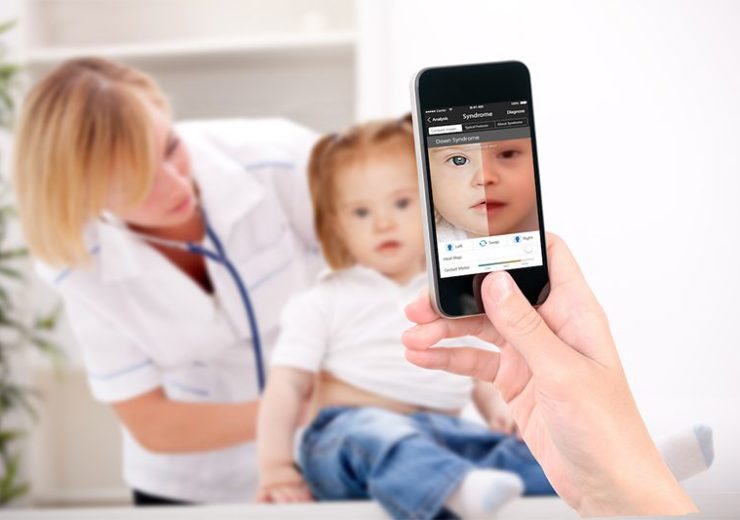
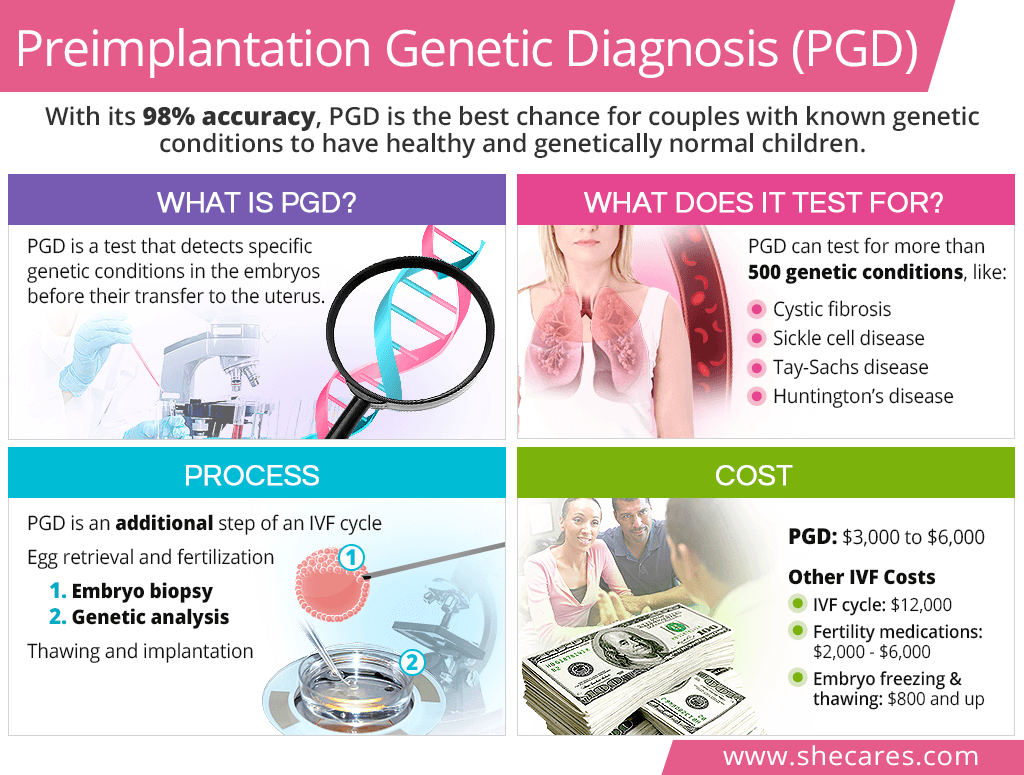
They are difficult to be precisely diagnosed by conventional clinical tests due to the. Preimplantation testing, also called preimplantation genetic diagnosis (pgd), is a specialized technique that can reduce the risk of having a child with a particular genetic or chromosomal disorder. We all have 46 chromosomes in our cells.
Lauri’s daughter, christy, a genetic counselor at mayo clinic, was instrumental in getting lauri the testing she needed for an accurate diagnosis. Genetic tests examine a person's dna in a variety of ways to assess a person's genetic health. Laboratory tests, including genetic testing:
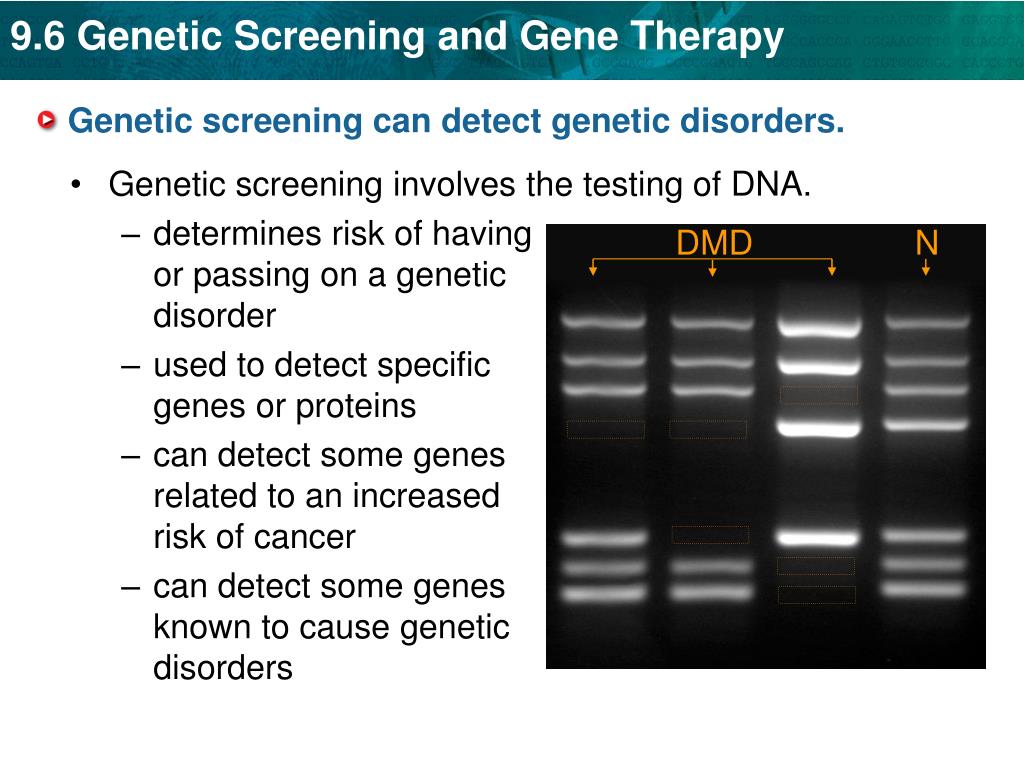
Presymptomatic genetic testing can tell if a person with a family history for a genetic disease but does not have symptoms or has a genetic alteration associated with the disease. Mutations in dna can result in genetic disorders. How are genetic disorders identified?
Help to diagnose a rare health condition in a child. The approach to genetic testing is individualized based on your medical and family history and what condition you’re being tested for. The tests evaluate a person's specific genetic risk for conditions like atrial fibrillation, breast cancer, kidney disease, heart disease, high cholesterol.
They are all designed to identify a particular gene that may cause a genetic disorder. Genetic disorders are conditions that occur as a result of changes to or mutations in dna within the body’s cells. Genetic disorders can be caused by a mutation in one gene (monogenic disorder), by mutations in multiple genes (multifactorial inheritance disorder), by a combination of gene mutations and environmental factors, or by damage to chromosomes (changes in the number or structure of entire chromosomes, the structures that carry.
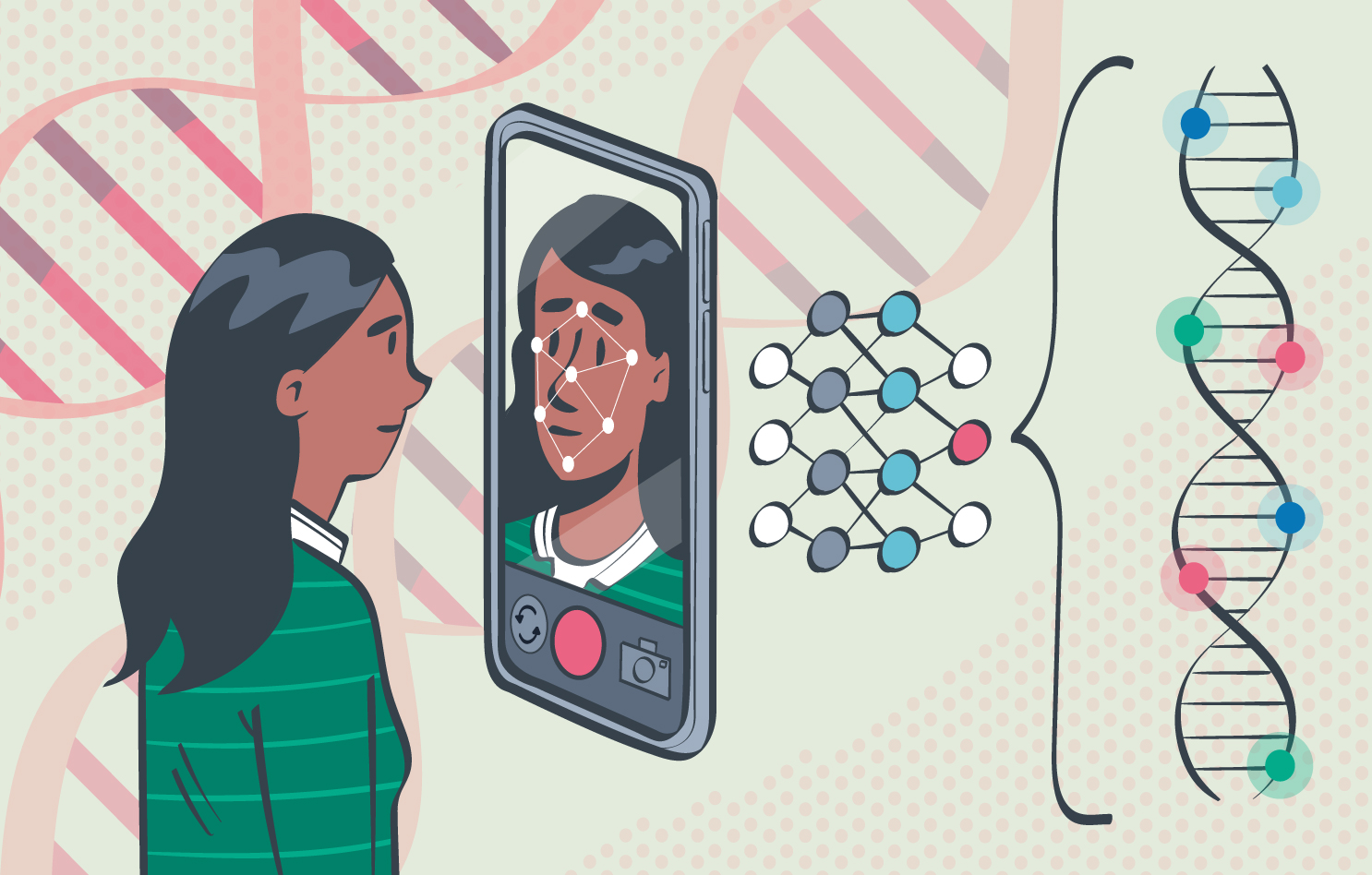
As the use of polygenic risk scores grows, one major concern is that the genomic datasets used to. Some of these variations can help doctors diagnose genetic disorders. The clinicians should be able to recognize and categorize genetic disorders and affected patients on the basis of symptoms and signs to a subtype of chromosomal or single gene disorders, so that they could offer an.
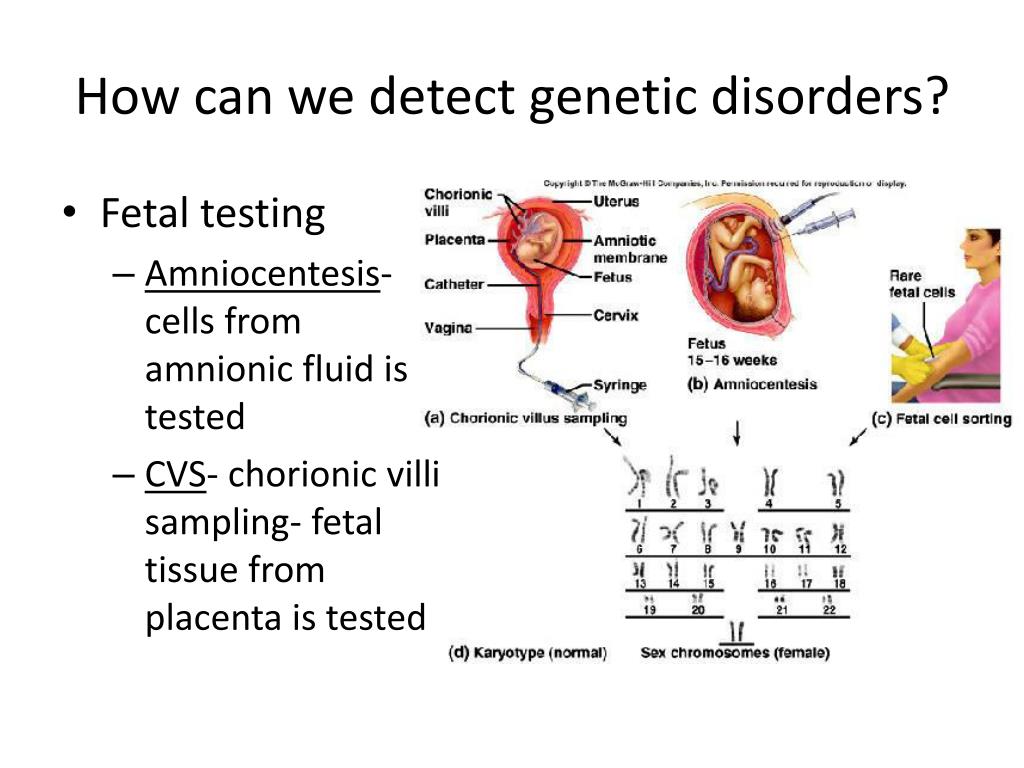
Detecting genetic abnormalities. Identifying a genetic disease finding the right specialist. Single gene tests look for.
Although human genetic diseases are rare, they account for an important public health burden [1, 2].diagnostic approaches to detect the underlying genetic causes of these diseases require a broad spectrum of technologies, ranging from traditional approaches such as karyotyping, genomic microarrays, fish, mlpa, and sanger. Predictive or predispositional genetic testing can identify individuals at risk of getting a disease prior to the onset of symptoms. Lose muscle mass and thus the ability to do.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2860730_color-5babc8d9c9e77c002ccae708.png)